Appearance
Python code blocks
Supersimple's Python blocks let you run arbitrary Python code, including accessing data from other blocks in the same exploration.
TIP
Code blocks are a convenient way for engineers to share the results of more advanced work with the rest of their teams, without needing others to set up full coding environments.
Usage
Create a new Python block via the "New block" button, and choose Python from the Code dropdown.
New Python blocks are prefilled with a few useful snippets that you can reuse, or delete and start from scratch.
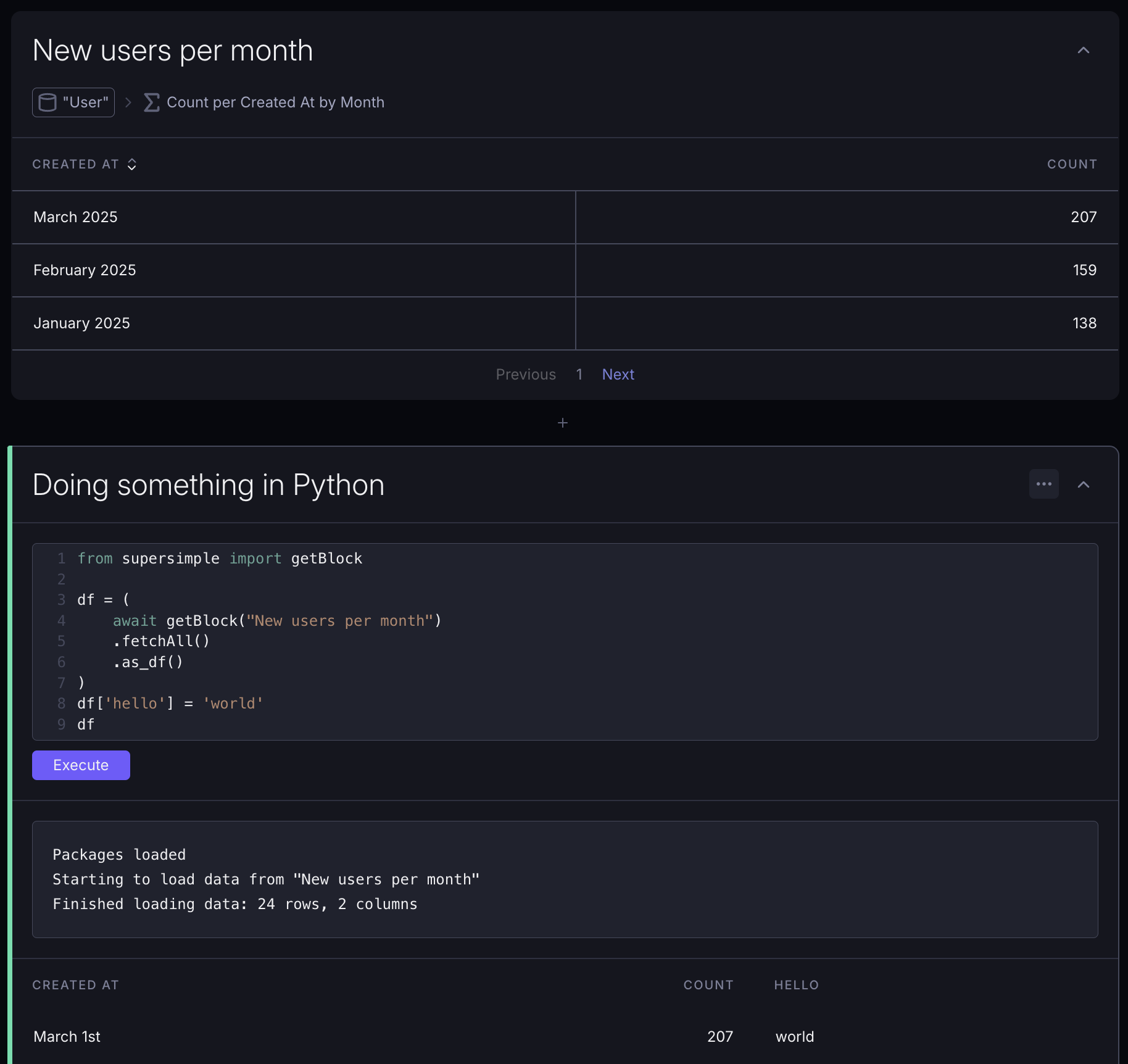
Using data from other blocks
You can access data from other blocks in your exploration using getBlock from the auto-included supersimple package:
python
from supersimple import getBlock
df = (
await getBlock("User") # data model name or block title
.fetchAll()
.as_df()
)fetchAll also supports optional parameters for pagination and retrieving a smaller set of fields
python
df = (
await getBlock("Event")
.fetchAll(page_size=100, limit=250, columns=['Event ID', 'Time', 'Type'])
.as_df()
)Packages
Python blocks come with a set of pre-installed packages, including pandas, numpy, and matplotlib. See the full list in Pyodide's docs. You can import these directly in your Python blocks.
python
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# use pandas and numpy as usualYou can install new Python packages from PyPI by invoking !pip install in the code block. Only non-native packages are supported.
python
# plotly does not come pre-installed, so we need to install it before using it
!pip install plotlyOutputting data
Similarly to Jupyter notebooks, the last expression in a Python block is automatically outputted as the block's result. Dataframes are automatically converted to Supersimple tables.
